Genus: Elettaria
|
Habitat: |
Native to southeastern Asia from India south to Sri Lanka and east to Malaysia and western Indonesia, where it grows in tropical rainforests. In India, the states of Sikkim and Kerala are the main producers of cardamom. |
Feature: |
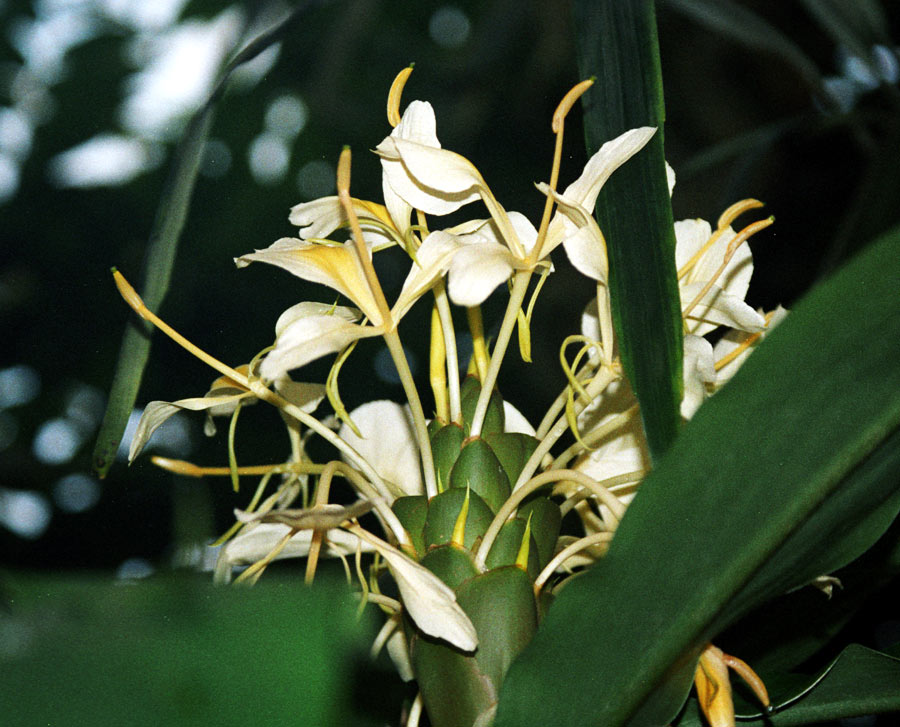
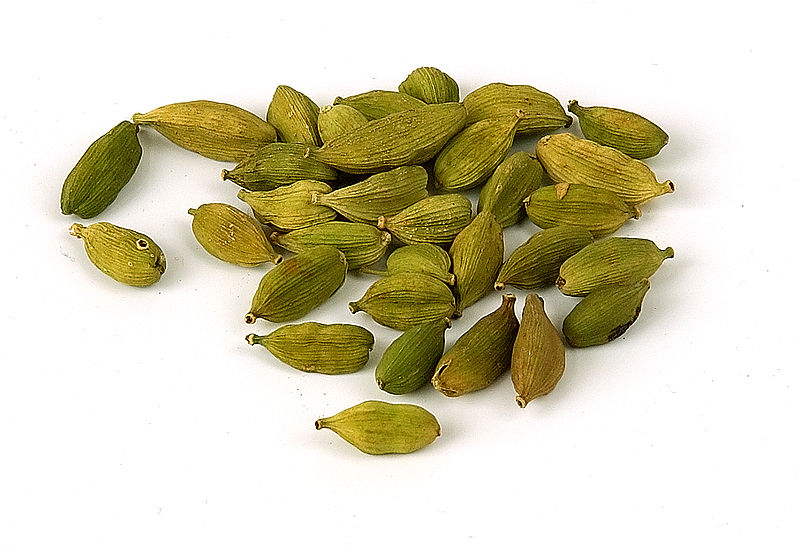
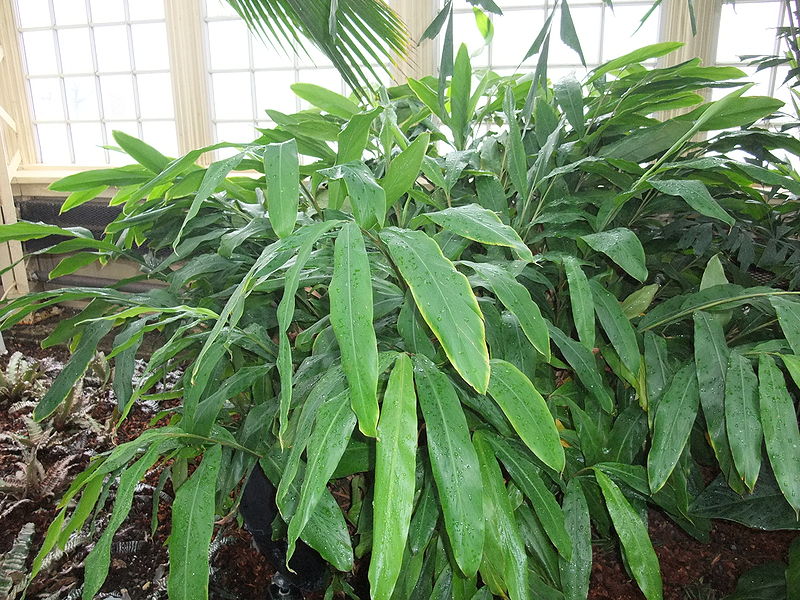
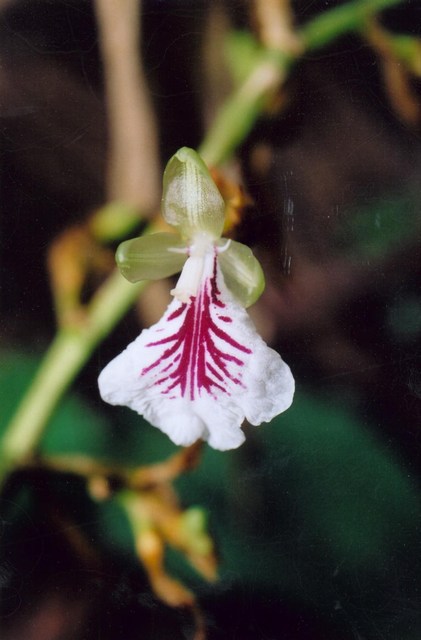
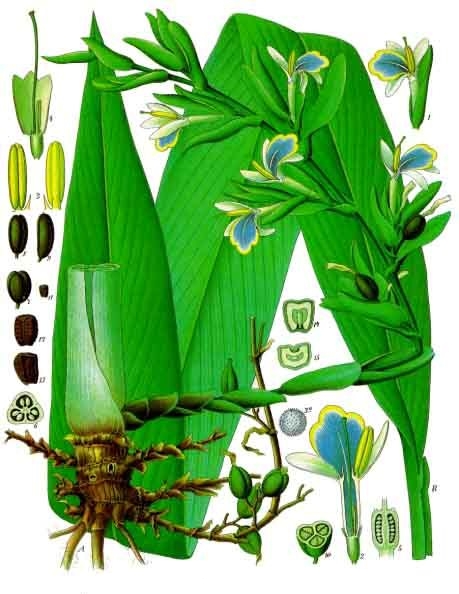
It is a pungent aromatic herbaceous perennial plant growing to 2–4 m in height. The leaves are alternate in two ranks, linear-lanceolate, 40–60 cm long, with a long pointed tip. The flowers are white to lilac or pale violet, produced in a loose spike 30–60 cm long. The fruit is a three-sided yellow-green pod 1–2 cm long, containing several black seeds. The essential feature of the inflorescence of Elettaria is a prostrate axis bearing 2-ranked sheathes with a cincinnus in the axil of each. Floral characters are similar to Amomum, but strikingly different in the nature of inflorescence. The genus Elettariopsis is very closely related to Elettaria. |
Economic Importance: |
Ground cardamom is an ingredient in many Indian curries and is a primary contributor to the flavour of masala chai. In Iran, cardamom is used to flavour coffee and tea. In Turkey, it is used to flavour the black Turkish tea, kakakule in Turkish. |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medicinal Importance: |
It is used internally for indigestion, nausea, vomiting and pulmonary disease with copious phlegm. It can be used with a laxative to prevent stomach pain, griping, as well as flatulence. | ||||||
Classification
| Elettaria | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Elettaria | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Subkingdom: | Viridaeplantae |
| Infrakingdom: | Streptophyta |
| Division: | Tracheophyta |
| subdivision: | Spermatophytina |
| Infradivision: | Angiospermae |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Superorder: | Lilianae | Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Elettaria |



Related publications
1) Ethnomedical uses of Zingiberaceous plants of Northeast India. Tushar, Basak S, Sarma GC, Rangan L. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Oct 28;132(1):286-96
2) Alpinia: the gold mine of future therapeutics. Ghosh S, Rangan L, 3 Biotech. 3: 173-185

