Department of Computer Science & Engineering, IIT Guwahati
Admission Session: December (2022 - 2023)
Schedule
 Interview Date: 6th - 7th December 2022.
Interview Date: 6th - 7th December 2022.
 Starting date of applications: ../../....
Starting date of applications: ../../....
 End date of receiving applications: ../../....
End date of receiving applications: ../../....
 Short-listing the candidates for written test and/or interview: ../../....
Short-listing the candidates for written test and/or interview: ../../....
 Sending of call letters for written test and/or interview: ../../....
Sending of call letters for written test and/or interview: ../../....
 Written test date & location: ../../....
Written test date & location: ../../....
 Interview date & location: ../../....
Interview date & location: ../../....
 Result declaration: ../../....
Result declaration: ../../....
For any queries please contact us at cseadmissions @ iitg.ac.in
Admissions to the Ph.D. Programme (December 2022)
Important Note
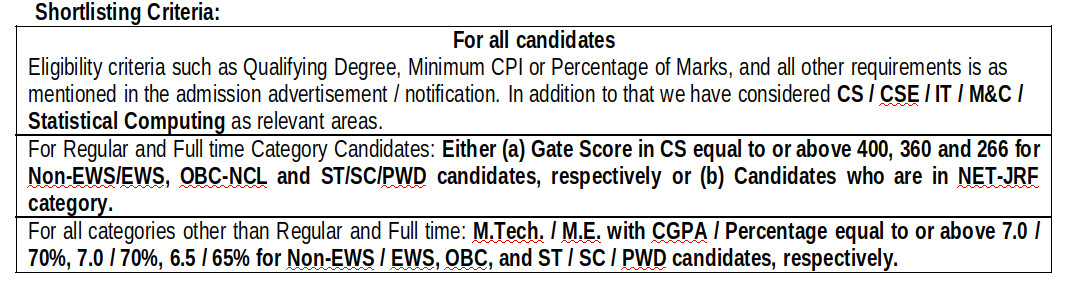
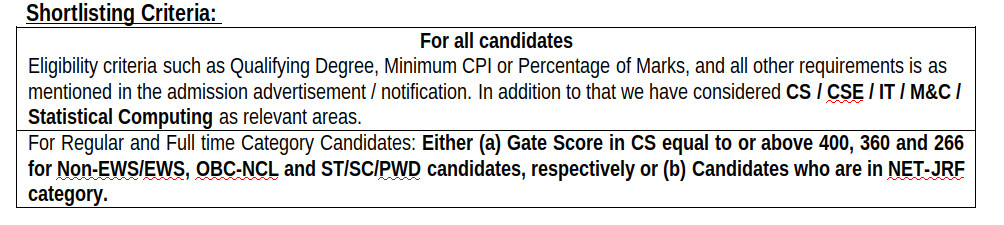
The CSE department has approximately equal number of Ph.D. vacancies in each diverse research areas (like Theoretical Computer Science, Computer Architecture and Embedded Systems, Computer Networks and Security, Machine Learning and Data Mining, Distributed Systems, and Man-Machine Interfaces) and detail of these research area available at https://www.iitg.ac.in/cse/cseresearchgroups Selection Criteria: Selection criteria are in general based on performance in tests and/or interviews in basic subjects of CSE (mentioned in the GATE syllabus) and your mentioned research area.
Based on our past experience, most of the Ph.D. applicants mention buzz words as their preferred research areas, so the area wise applicant distribution is skewed. Statistics of the previous admission is given as follows:
As we invite application for Ph.D. for all the multiple diverse research areas of our department and department has an approximately equal number of Ph.D. vacancies in multiple diverse research areas. If a Ph.D. applicant mentions popular areas as his/her area of interest then his/her chances of getting selected will be less due to heavy competition in that specific research area.
Admission Process
Syllabus
CSE @ IIT Guwahati
The benefit of joining Ph.D. CSE @ IIT Guwahati are (a) Scholarship for Ph.D. is higher than M.Tech, (b) Ph.D. is a highest academic degree and it gets the highest respect in the community, you may not require any other degree (intermediate M Tech degree) after this, (c) you can proudly put Dr before your name. (d) you have options to choose both industry job as well as the stable academic job, (e) will be able to do high-quality publications in the reputed journals/conferences, (f) eligible for PMRF and Industry fellowships during the Ph.D., (g) for a sincere and hardworking student, one can finish Ph.D. in within four to five years.
 List of Ph.D. alumni and their placement detail are available at http://www.iitg.ac.in/cse/researchscholarscompleted
List of Ph.D. alumni and their placement detail are available at http://www.iitg.ac.in/cse/researchscholarscompleted
 Detail about Ph.D. program CSE @IIT Guwahati available http://www.iitg.ac.in/cse/phdcse
Detail about Ph.D. program CSE @IIT Guwahati available http://www.iitg.ac.in/cse/phdcse