
WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING LABORATORY
Department of Civil Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler

An acoustic Doppler current profiler (ADCP) is a hydroacoustic current meter similar to sonar, attempting to measure
water current velocities over a depth range using the Doppler effect of sound waves scattered back from particles
within the water column. ADCPs contain piezoelectric transducers to transmit and receive sound signals.
Acoustic Doppler velocimeter
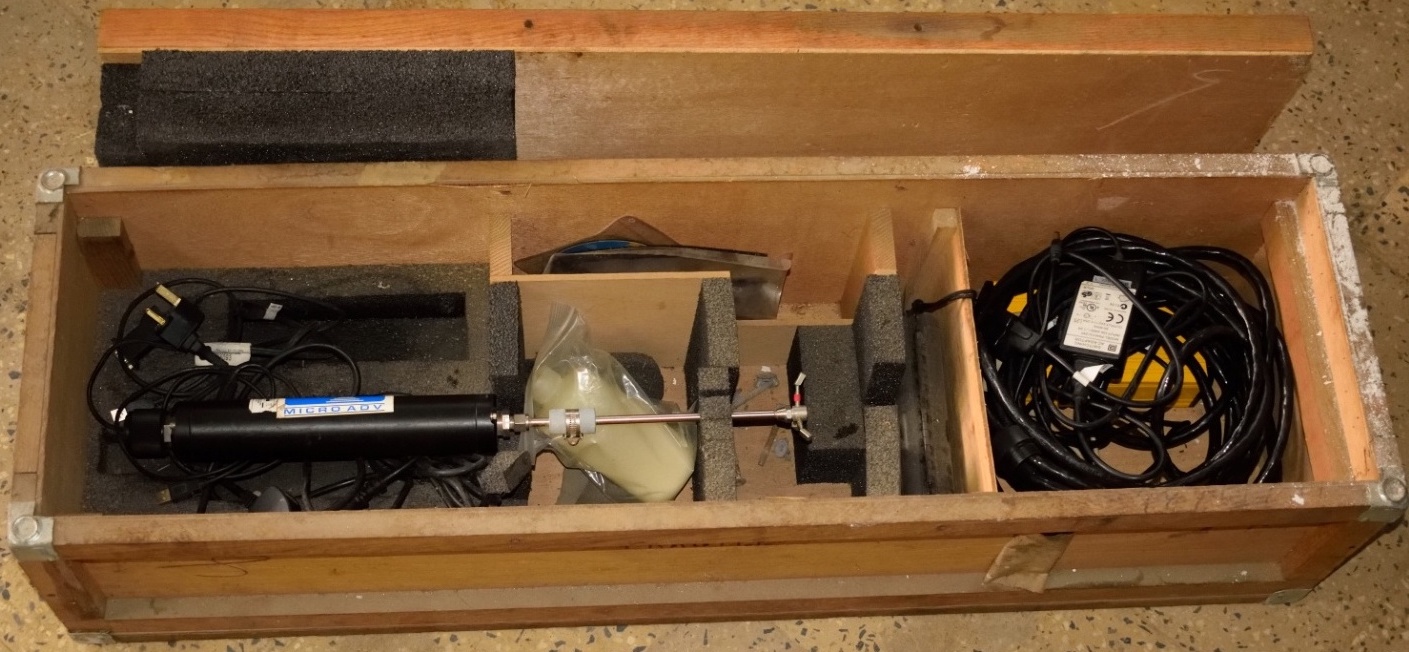

ADV records instantaneous velocity components at a single-point with a relatively high frequency. Measurements
are performed by measuring the velocity of particles in a remote sampling volume based upon the Doppler shift effect.
Area Velocity Flow Meter
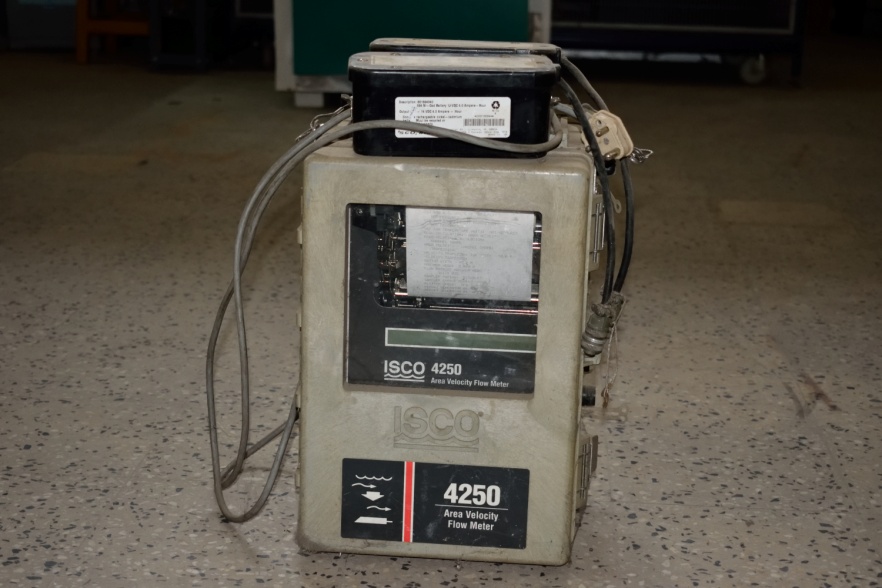

An Area-Velocity Flow Meter is used to monitor flow volume in an open channel or pipe (partially full sewer pipes
and surcharged pipes etc.). It can measure both Level and Velocity continuously for volume calculation. An ultrasonic
signal is continuously injected into the water and Doppler's principle is used to measure flow velocity.
Basic Wind Tunnel
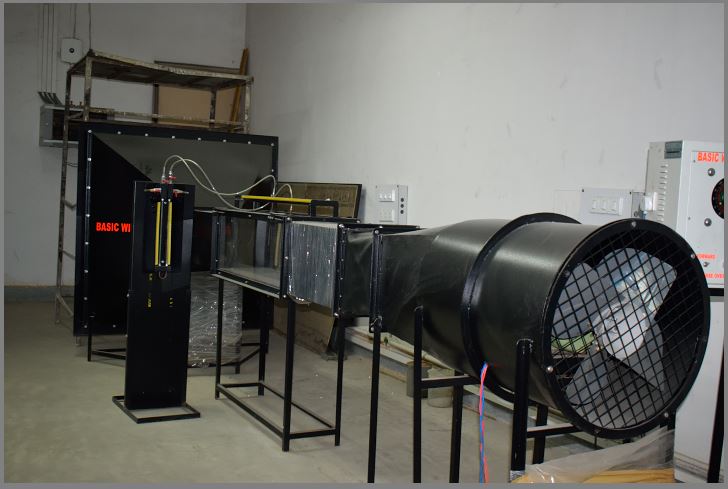

Basic wind tunnel is used to understand the difference between lift and drag. How lift is related to velocity and
how the angle of attack of an air foil changes the amount of lift; all these studies can be made using a wind tunnel.
Bernoulli's Apparatus
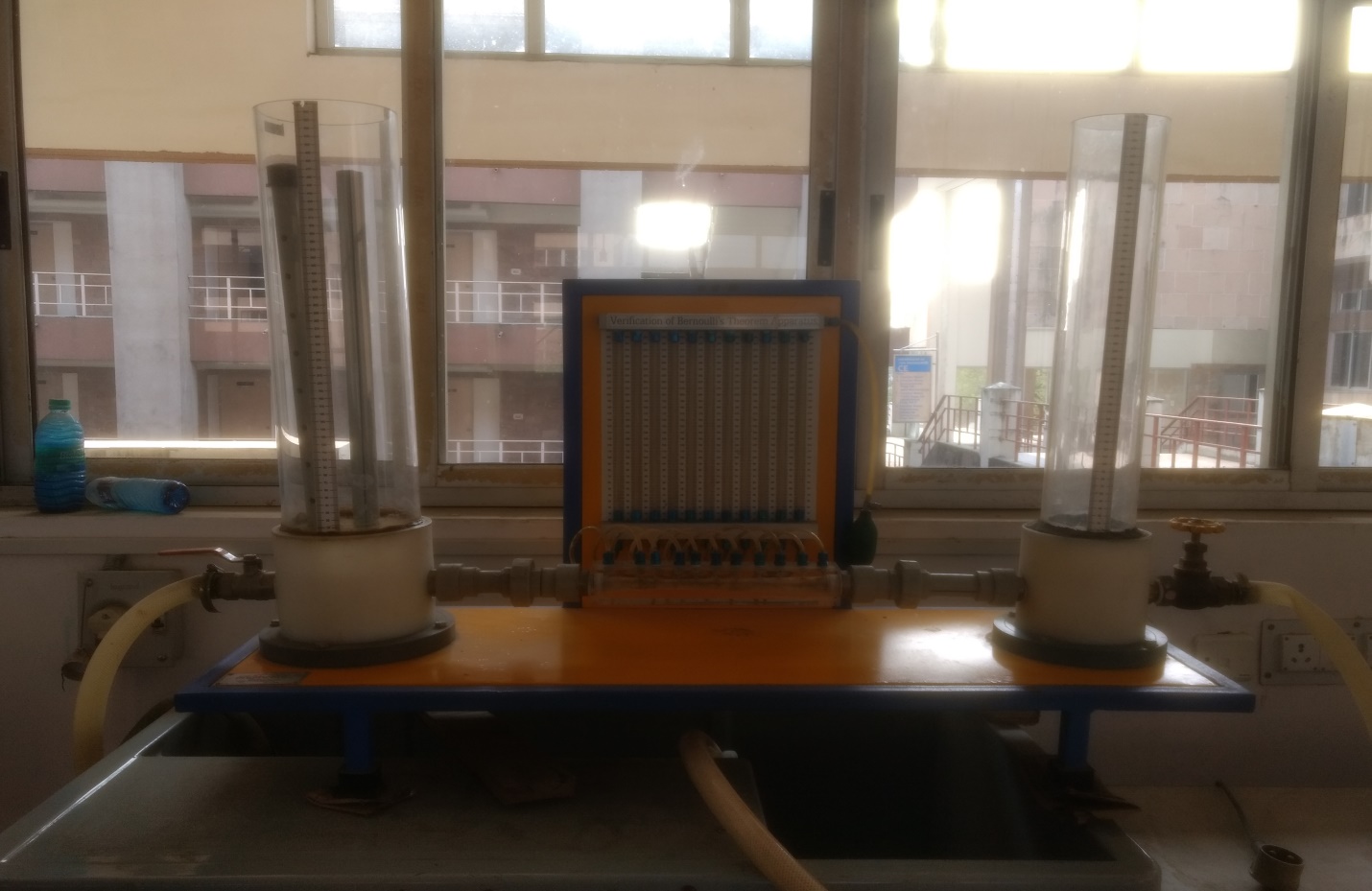

This apparatus is used to verify the Bernoulli's theorem by calculating the energy & head of water at different
section. According to the Bernoulli's theorem of fluid flow through a pipe, the total head at any cross section
is constant (based on certain assumptions) .However, in a real flow due to friction and other imperfections,
as well as measurement uncertainties, the results will deviate from the theoretical ones.
Cavitation Apparatus

The purpose of the Experiment is to observe the phenomenon of Cavitation in a liquid (by reducing the liquid to its
vapour pressure).
Cavitation can affect the performance of hydraulic machinery such as pumps, turbines and propellers,
and the impact of collapsing bubbles can cause local erosion of metal surfaces.
Determination of Minor Losses in Pipes
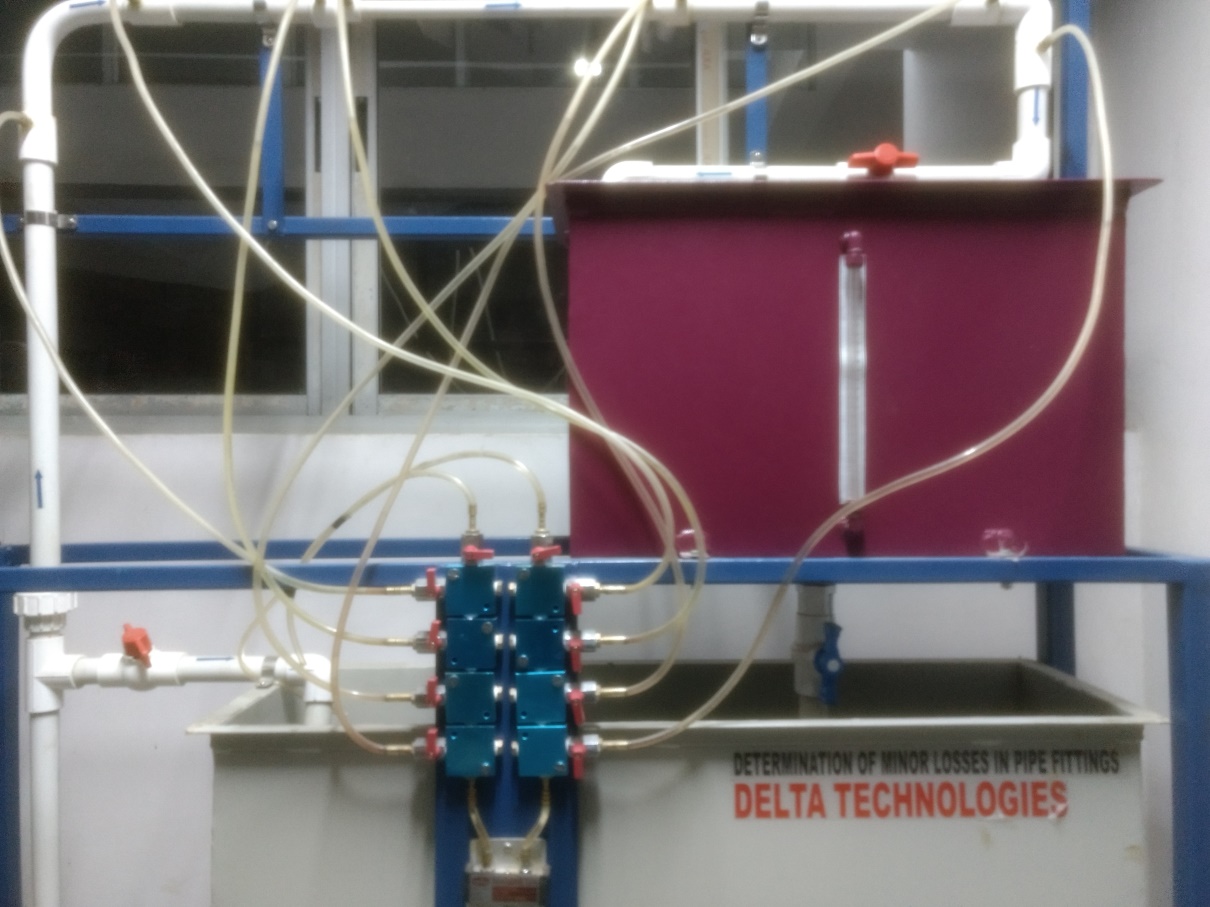
The loss of energy due to change of velocity of the flowing fluid in magnitude or direction is called minor loss of energy.
The minor loss of energy includes these cases: (a) Sudden expansion of pipe (b) Sudden contraction of pipe (c) at the
entrance of pipe (d) At the exit of pipe (e) Bending in pipe.
Drainage and Seepage Tank
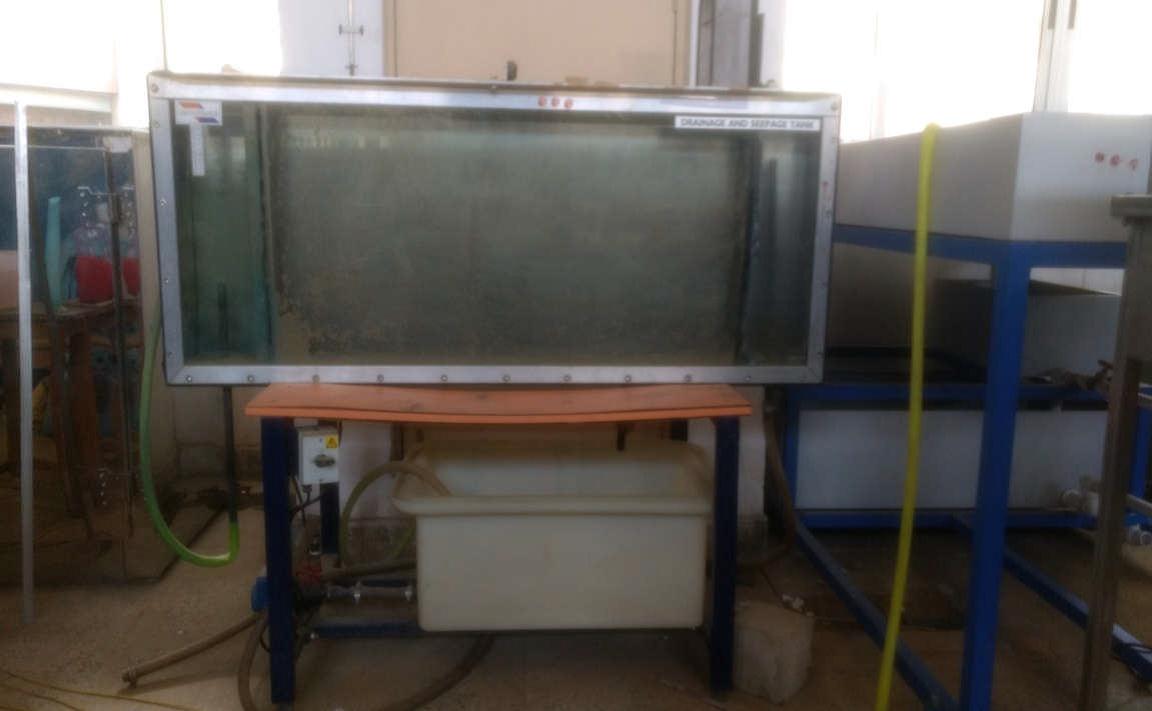

Drainage and Seepage Tank has been designed to allow students to make an experimental study of flow through permeable
media. It can be used to find flow line visualization, flow net construction, determining seepage rate, verification darcy`s law.
Echo Sounder
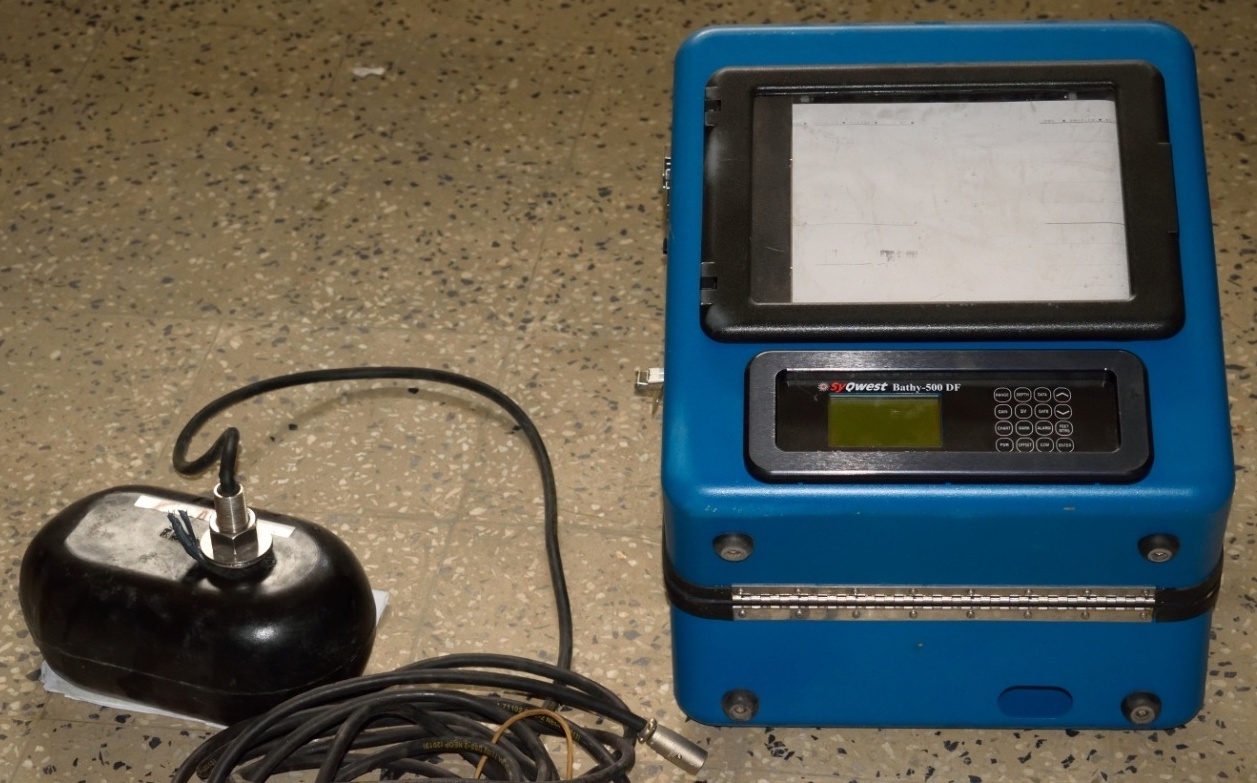

Echo Sounder is a rapid method of determining depth of water bodies. A sound impulse is transmitted (by a transmitter)
from the surface of water level to the bed of the river followed by receiving the reflected impulse in the form of echoes.
The time interval between emission and return of the reflected sound waves is recorded to estimate depth.
Five-Meter Flow Channel

This five-meters flow channel or flume is used mostly for carrying out experiments and demonstrations in water flow.
Friction in a uniform flow channel, flow over a sharp-crested weir, the broad-crested weir, flow under a sluice gate etc.;
all these demonstrations and studies can be carried out using this flume.
Flow Meter
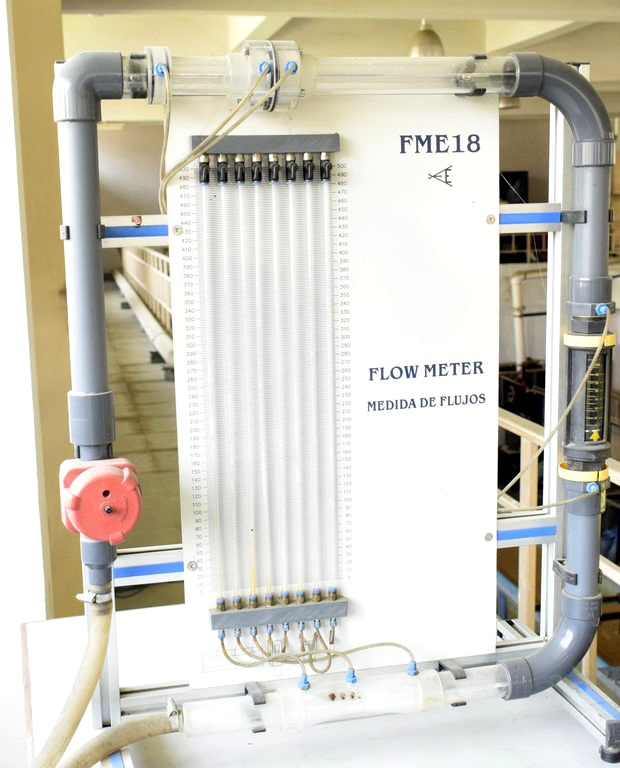

A flow meter is a device used to measure the flow rate or quantity of a gas or liquid moving through a pipe. Flow
measurement applications are very diverse and each situation has its own constraints and engineering requirements.
Fluid Friction Apparatus
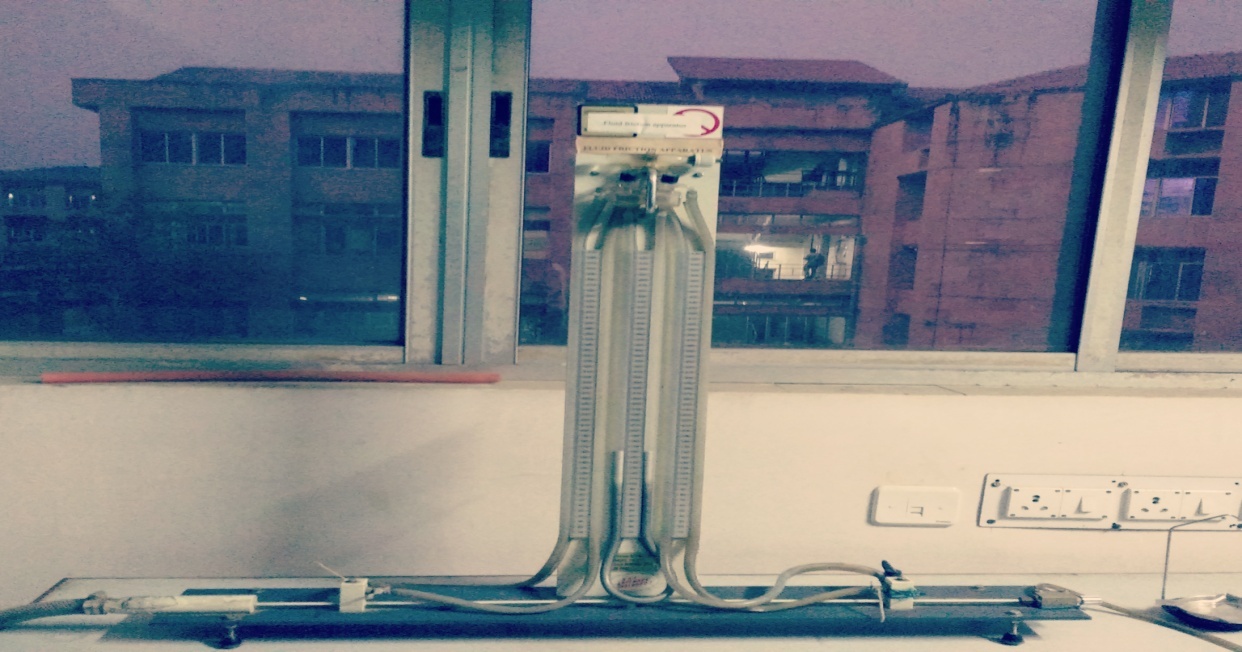

The fluid friction apparatus is designed to allow a detailed study of pressure drop as a result of fluid friction, when
an incompressible fluid flows through pipes, fittings, and flow metering devices.
Friction head losses in straight pipes
of different sizes can be investigated with a wide range of Reynolds number, covering laminar, transitional, and
turbulent flow regimes.
An artificially roughened tube is also incorporated into the apparatus to demonstrate the
departure from typical smooth bore pipe characteristics.
Flow over Weir Apparatus
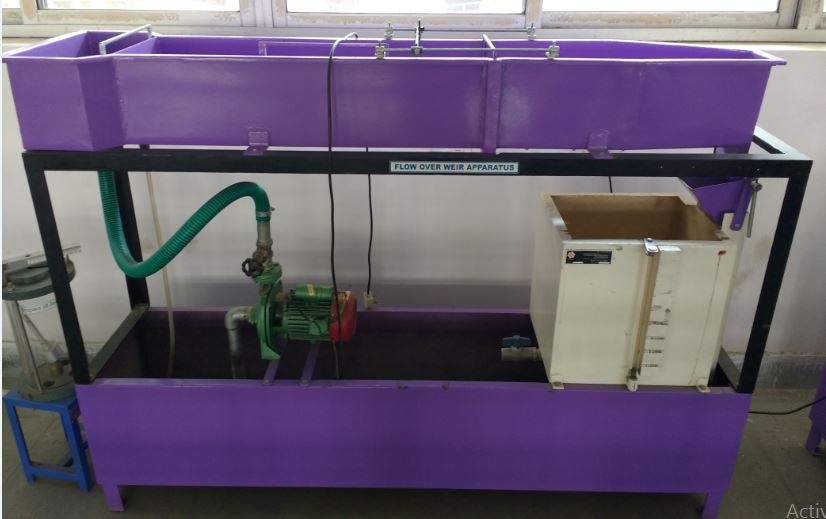

In most cases Weirs take the form of a horizontal barrier across the width of a river that pools water behind it whilst
still allowing it to flow steadily over the top.
Weirs are commonly used to prevent flooding, measure discharge and
help render rivers navigable.
Flow through Orifice & Mouth Piece
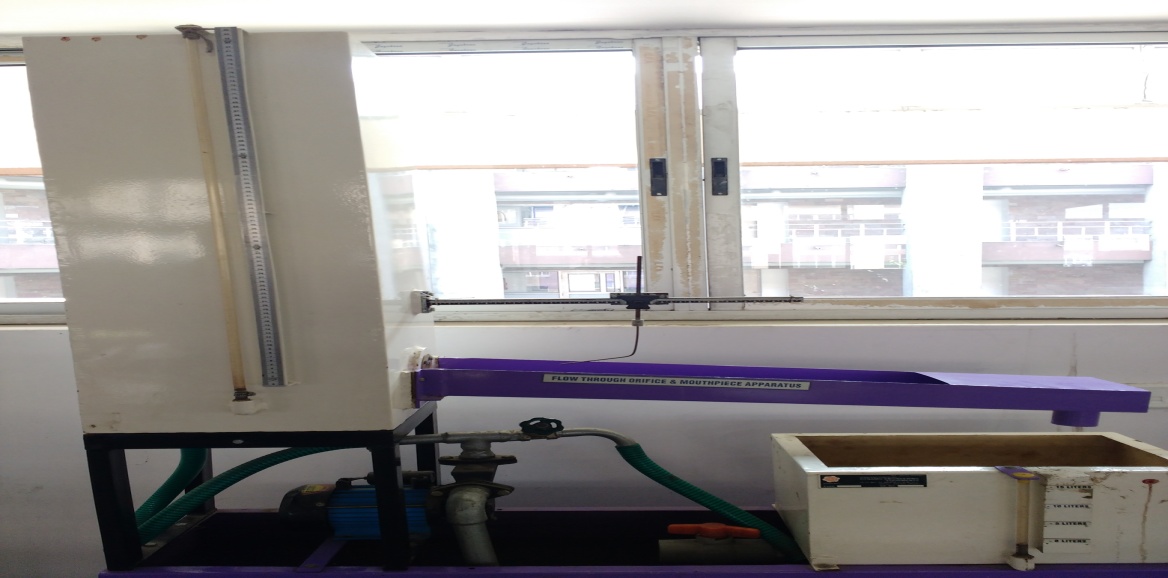

A mouthpiece is short tube fitted to a same size circular opening provided in a tank so that fluid may be discharged
through it.
Orifice and mouthpiece are used to measure the rate of flow of liquid. A measuring tank is provided to
measure the discharge.
Free and Forced Vortex Flow

The experimental procedure involves measurement of the resulting free surface that represents the variation of the
sum of the pressure head and datum head. An arrangement is provided to drain the vessel.
Flows where streamlines
are concentric circles and the tangential velocity is directly proportional to the radius of curvature are known as plane
circular forced vortex flows.
The flow field is described in a polar coordinate system as, All fluid particles rotate with
the same angular velocity w like a solid body.
Free vortex flows are the plane circular vortex flows where the total
mechanical energy remains constant in the entire flow field.
There is neither any addition nor any destruction of energy
in the flow field.
Therefore, the total mechanical energy does not vary from streamline to streamline.
Ground Water Flow Laboratory Model-3D
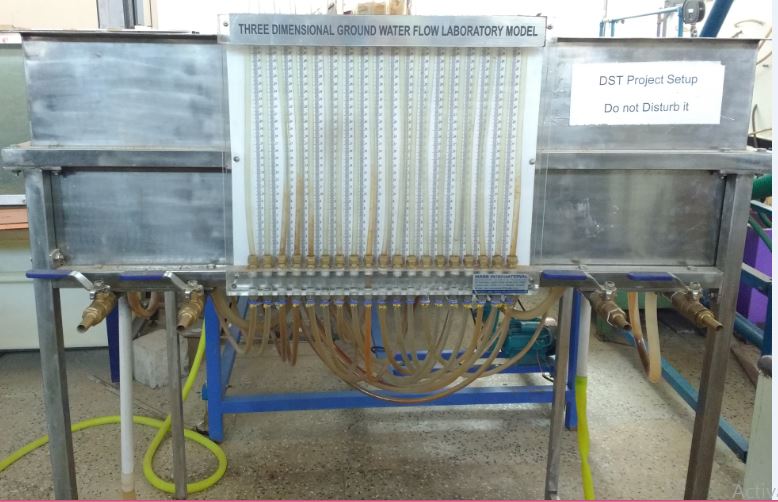

The applicability of a Groundwater model to a real situation depends on the accuracy of the input data and the
parameters.
Determination of these requires considerable study, like collection of hydrological data (rainfall,
evapotranspiration, irrigation, drainage) and determination of the parameters mentioned before including pumping
tests.
As many parameters are quite variable in space, expert judgment is needed to arrive at representative values.
Hydraulic Bench
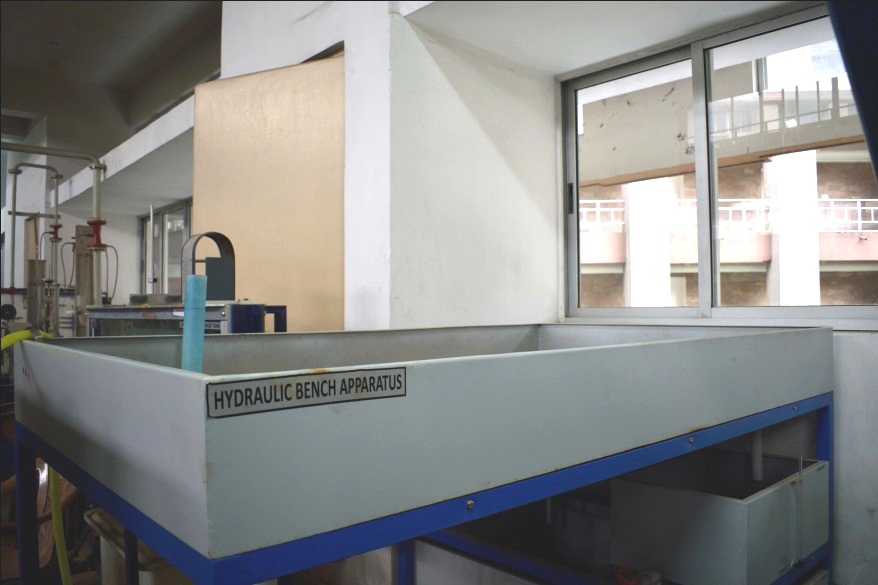

Hydraulic bench is a very useful apparatus in hydraulics and fluid mechanics. It is involved in majority of experiments
to be conducted e.g. To find the value of the co-efficient of velocity 'Cv',
coefficient of discharge 'Cd', to study
the characteristics of flow over notches, to find metacentric height, to find head losses through pipes, to verify
Bernoulli's theorem etc.
Hydrostatic Bench

Hydrostatic Bench is used to demonstrate the properties of fluids and their behaviour under hydrostatic or rest conditions.
It is equipped with all the apparatus needed for a complete range of experiments on properties of Newtonian fluids.
Impact of Jet Apparatus
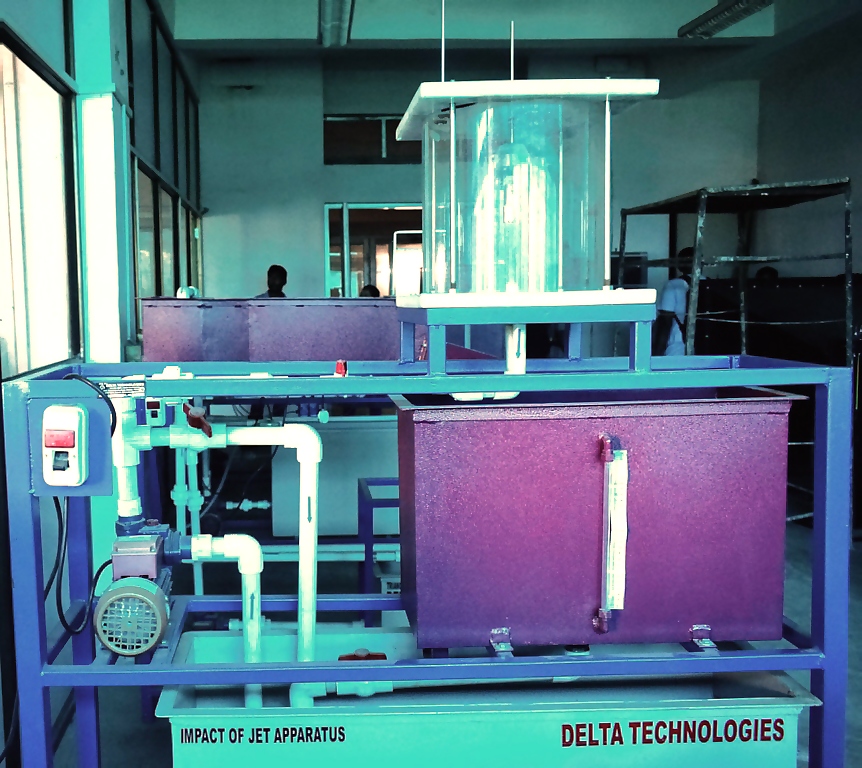
The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate the application of the momentum equation. The force generated
by a jet of water deflected by an impact surface is measured and compared to the momentum change of the jet.
Infiltrometers

Infiltrometer is a device used for determining water infiltration capacity of the soil and other porous media. Several
conventional (single ring and double ring) and disc infiltrometers (mini disc, tension disc etc.) are available for infiltration
measurement. Driving of rings in case of double ring and single ring distorts the soil structure which can be overcome
by using disc infiltrometers.
Losses In Pipe System

When a fluid flows in a closed conduit pipe, its energy loss can be demonstrated in this experiment. Fluid flow in
pipes is associated with many major (frictional losses) and minor (e.g. losses due to sudden contraction and expansion,
due to bends etc.) losses.
Open Channel Flume
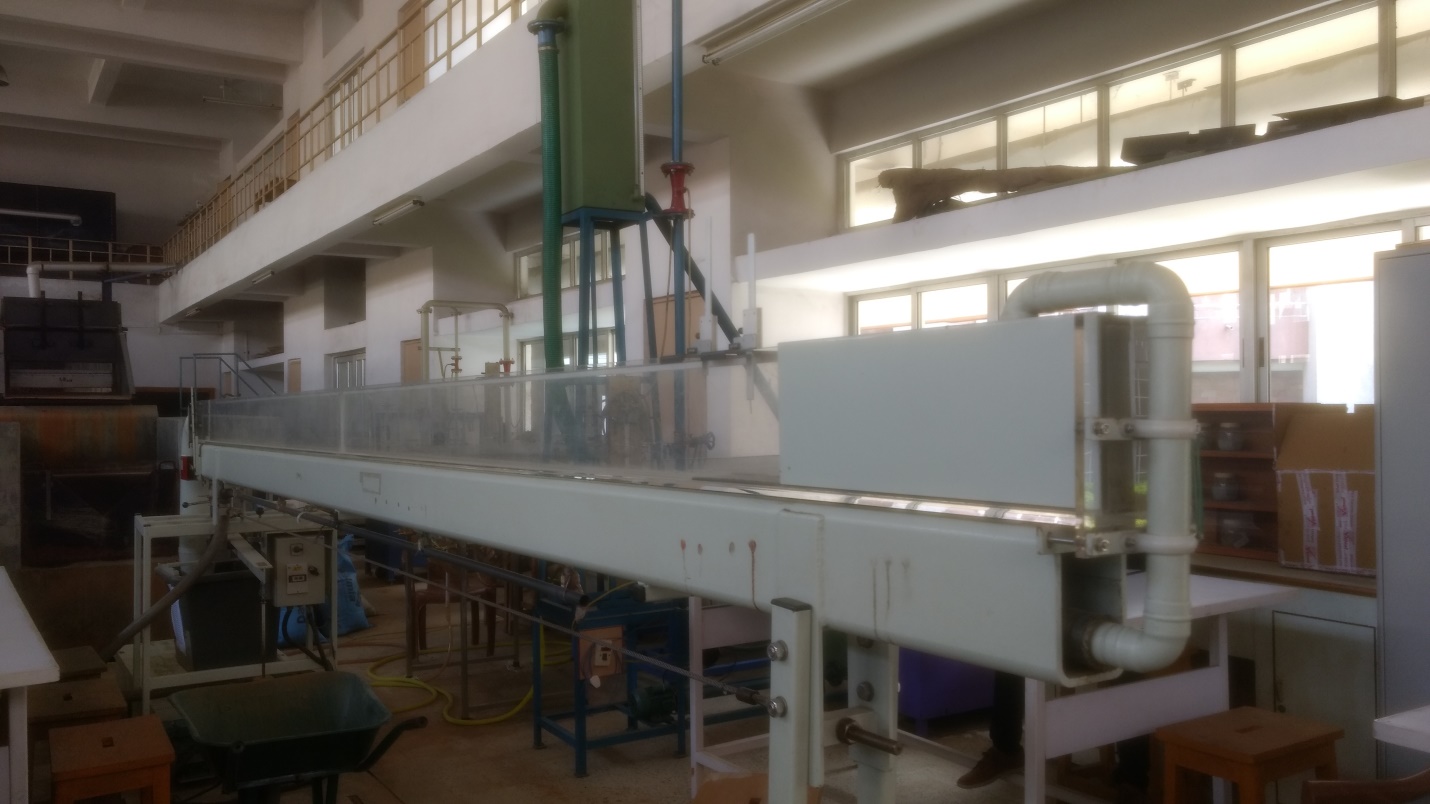

It is used to measure the flow of water in open channels; a flume is defined as a specially shaped, fixed hydraulic
structure that under free-flow conditions forces flow to accelerate in such a manner that the flow rate through the
flume can be characterized by a level-to-flow relationship as applied to a single head.
Open channel flow rate
measurement is usually done by measuring a change in water depth.
It can be done with a weir or flume. Common
types are the sharp crested weir (including V-notch weir, rectangular weir, and cipolletti weir), the broad
crested weir, the Parshall flume and venture flume.
Open Pan Evaporimeter
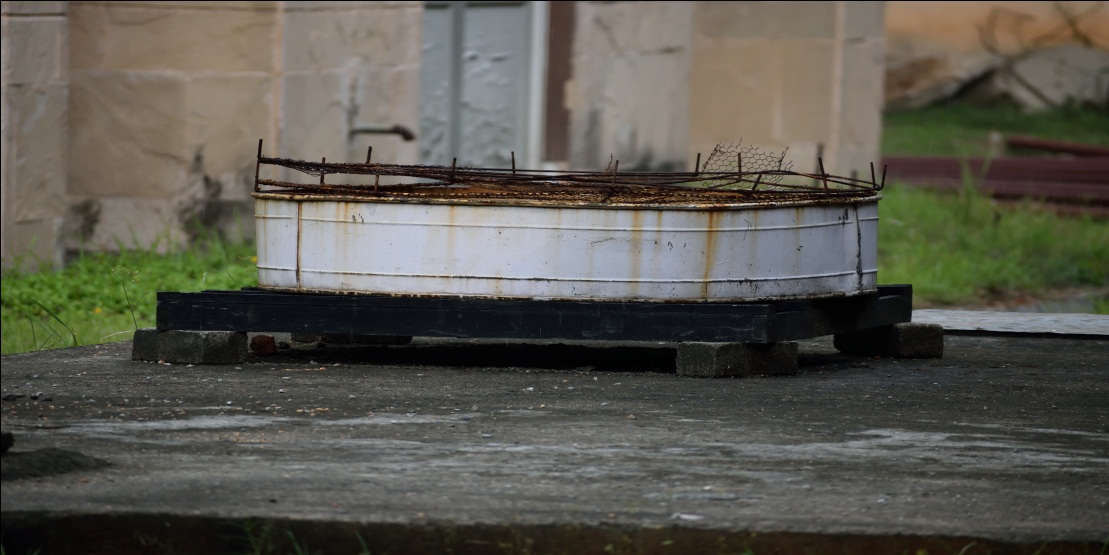

Pan Evaporimeter is used to measure the rate of evaporation of water into the atmosphere. Several factors affect
evaporation rate e.g. the water supply rate, the nature of the evaporating surface, wind speed, temperature etc.
Thus, the data collected by evaporimeter often do not reflect true evaporation processes making its use limited.
Pipe Friction Apparatus
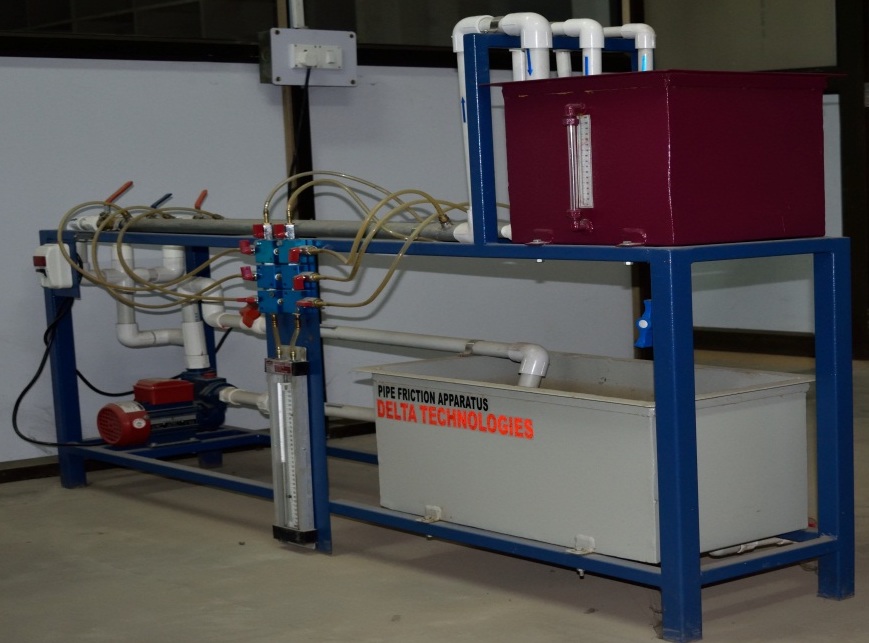

This apparatus is used to evaluate the friction factors defined by Darcy-Weisbach, Hazen-Williams, and Manning equations.
Its application enables determination of the friction factors in the experiment, which may also be applied with Moody's
diagram.
Pitot Tube
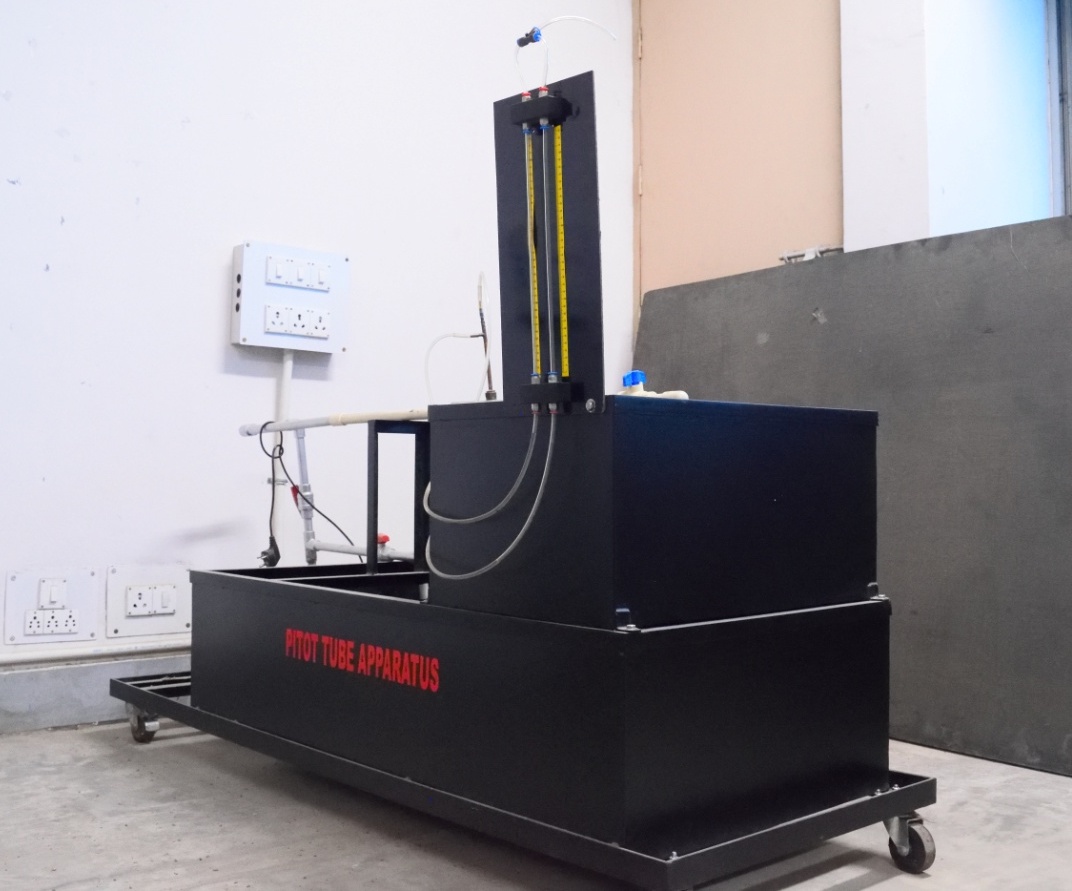

It is a pressure measurement instrument used to measure fluid flow velocity. It is widely used in industrial applications
to measure the local flow velocity at a given point in the flow stream.
Reynolds Apparatus
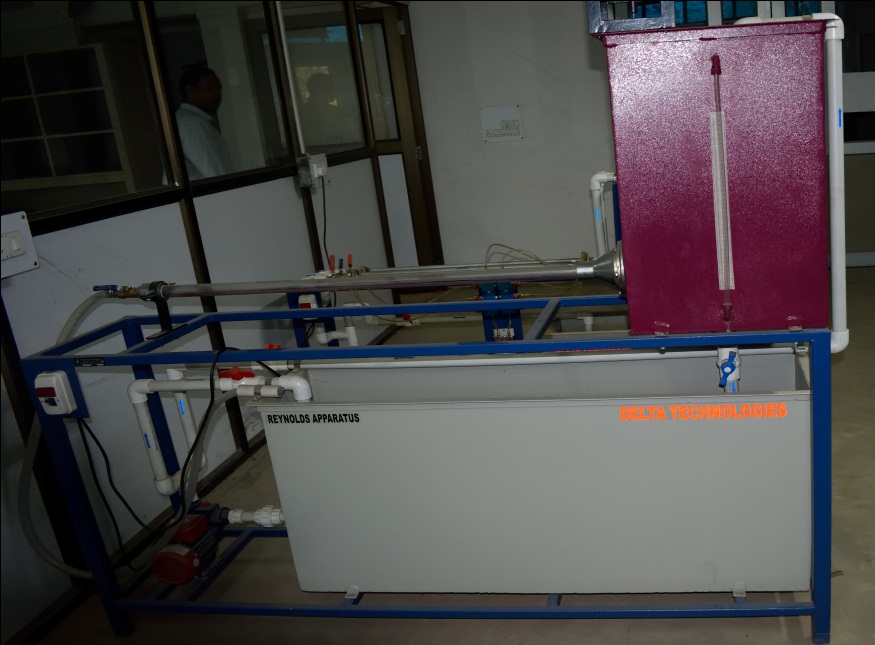

The Reynolds apparatus is used to study different types of flow. Conducted experiment is used to determine the
critical Reynolds number at which laminar flow becomes transitional, and transitional flow becomes turbulent.
Rainfall Simulator
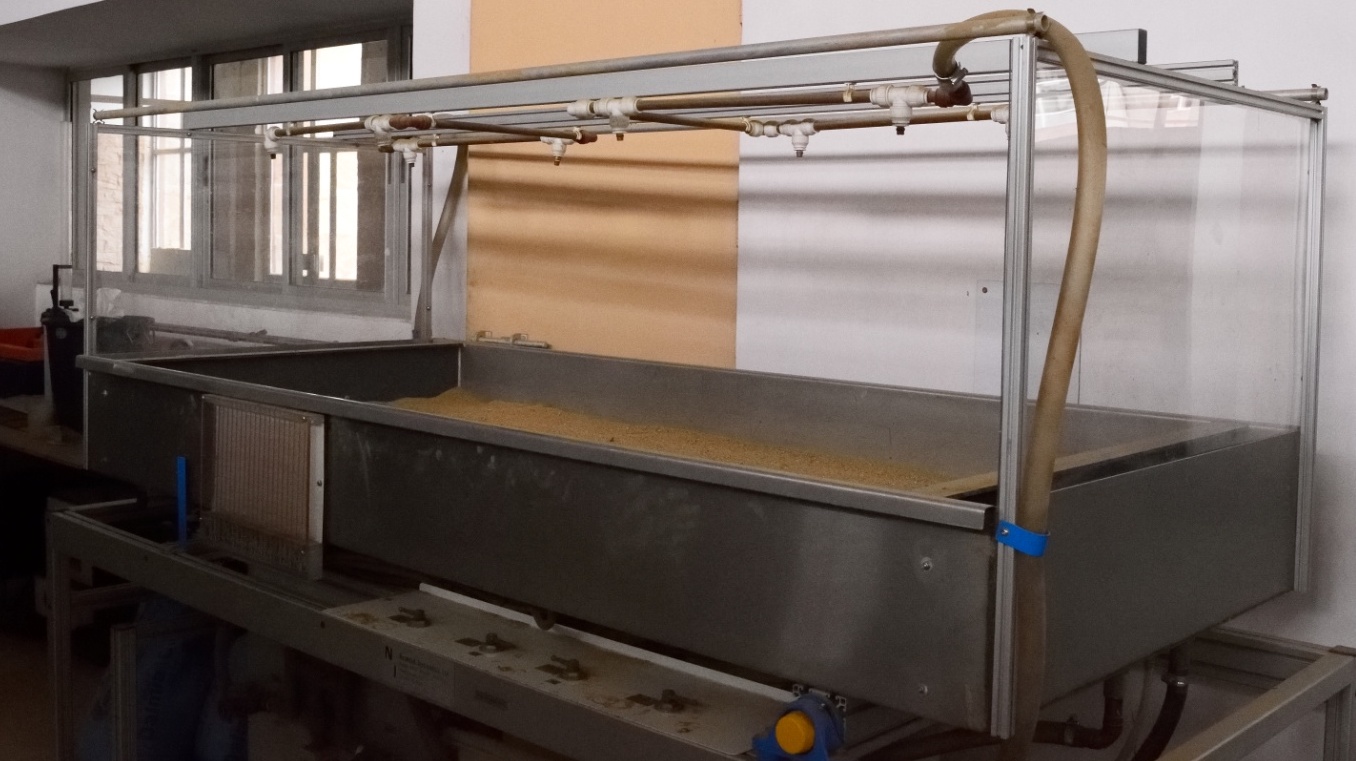

A rainfall simulator is an ideal tool for studying infiltration, soil erosion, and other processes. These are used to apply
uniform rainfall rates over land surfaces or packed soil boxes to evaluate runoff under controlled conditions. It offers
the advantages of quicker and simpler measurements without having to wait for natural rain. By working in the setup
with a constant and controlled rain, the unpredictability and unreliability of the natural rain can be eliminated.
Triangular And Rectangular Notch Tank Apparatus
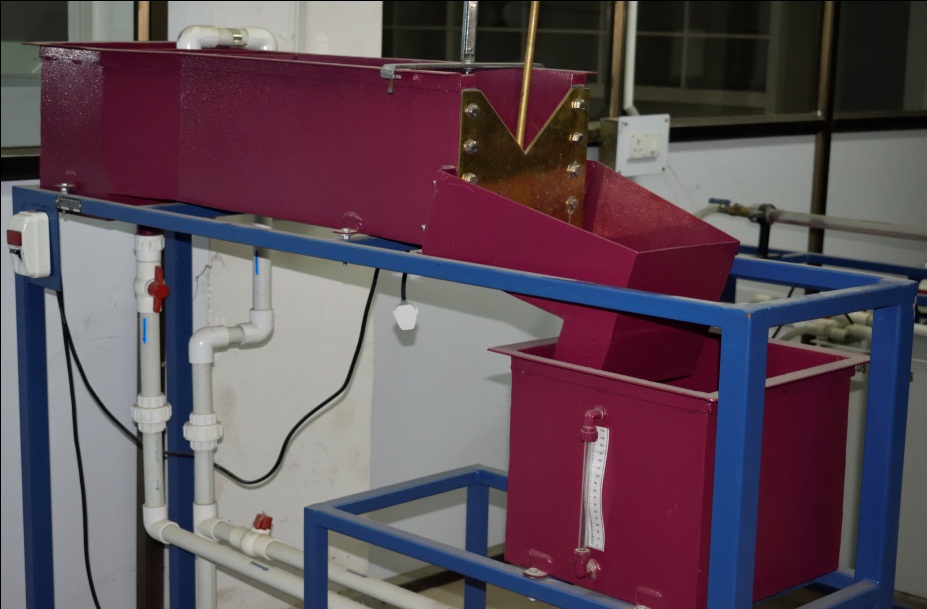

Notches are those flow structures whose length or crest in the direction of flow is accurately shaped and is used for
measuring the rate of flow of liquid through a small channel or a tank. In triangular notch head is large even for small
discharge. Hence, flow is not affected much by surface tension and viscosity. For small discharge triangular notch gives
more accurate result.
Universal Pump Test Rig
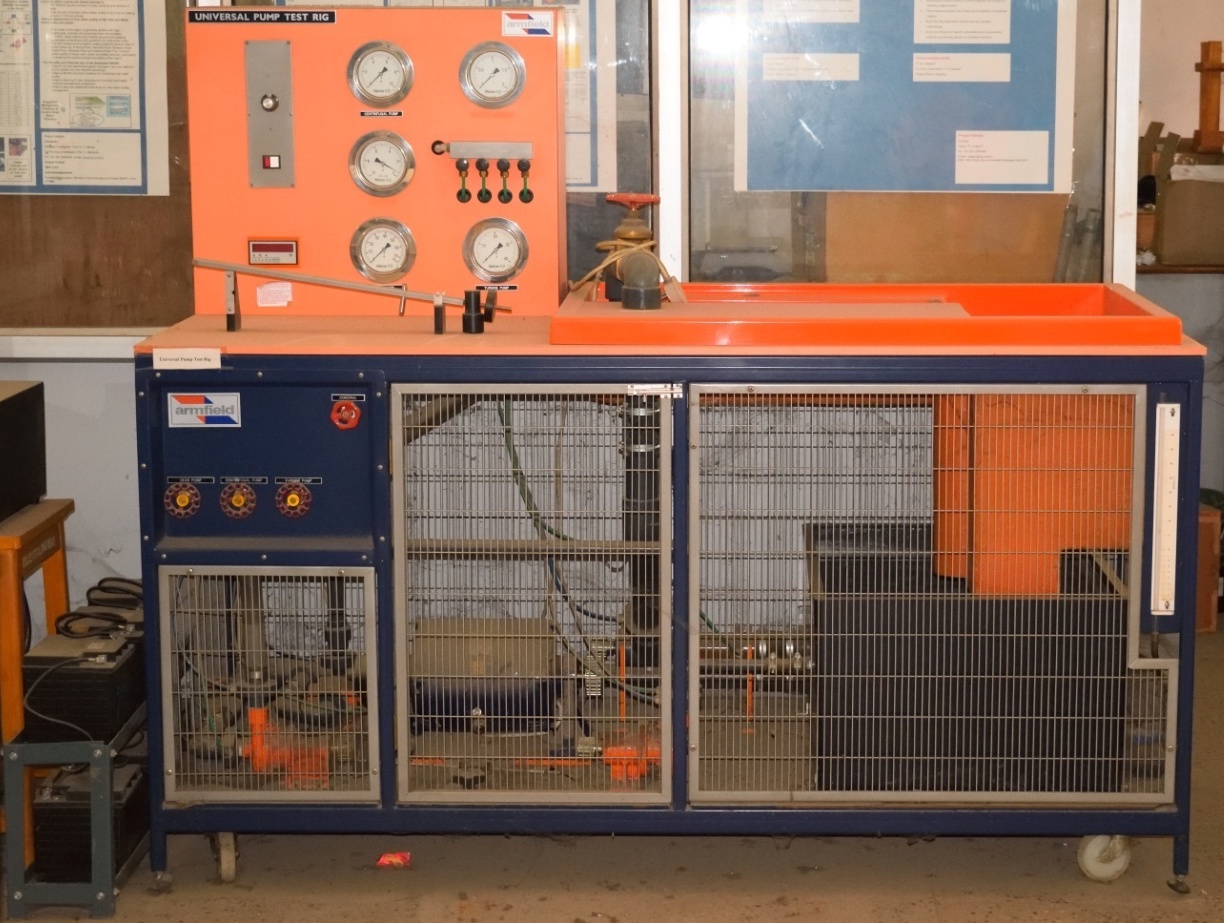

It is used to demonstrate the operating characteristics (headflow curves and efficiency) of a series of different types
of pumps, each having a broadly similar input ower.
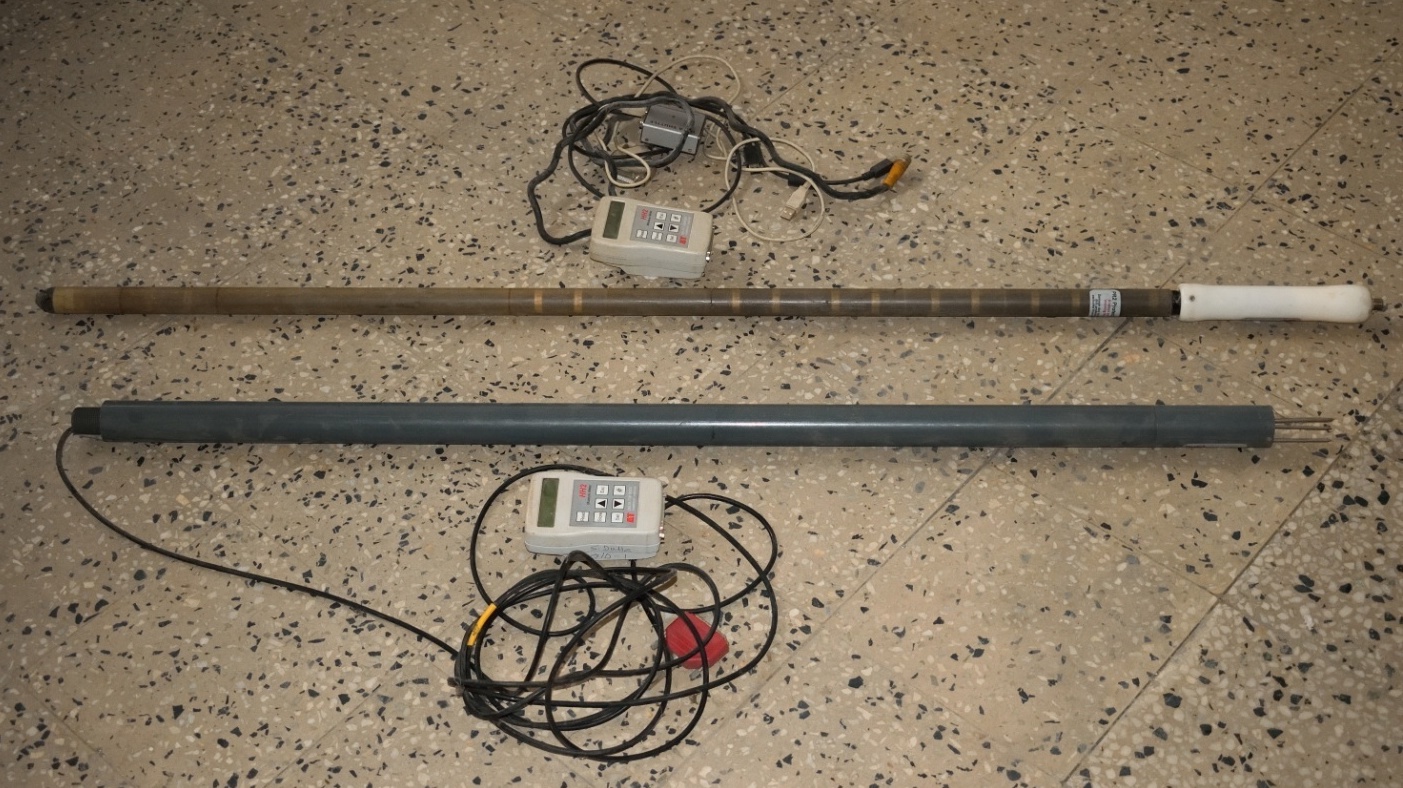
Sensors

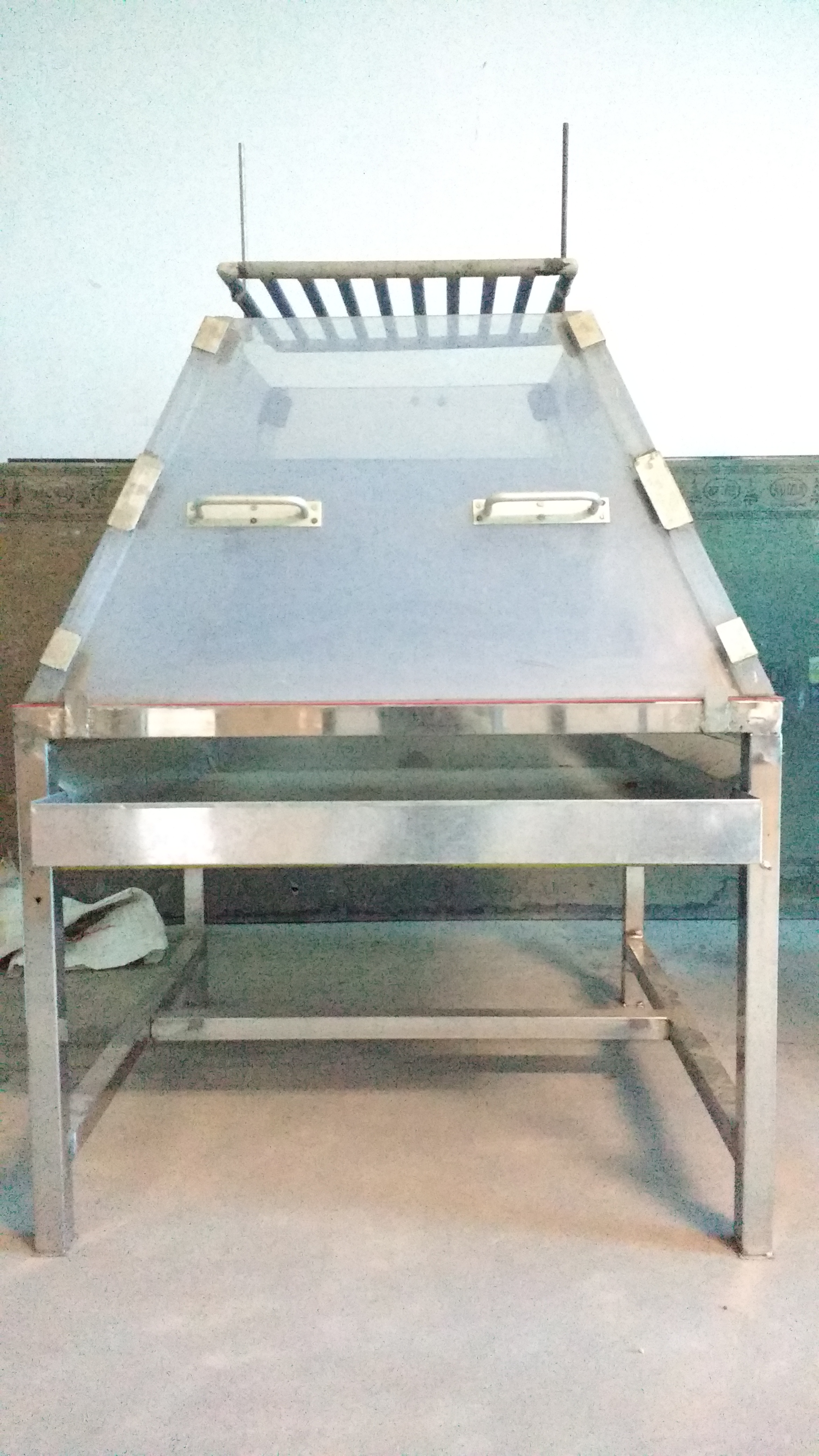
Landfill Leaching Model

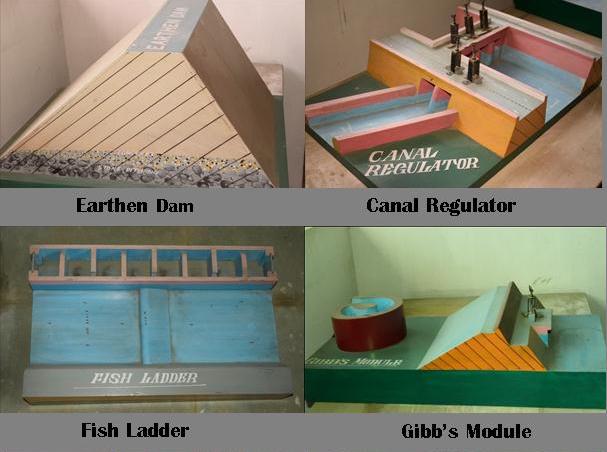
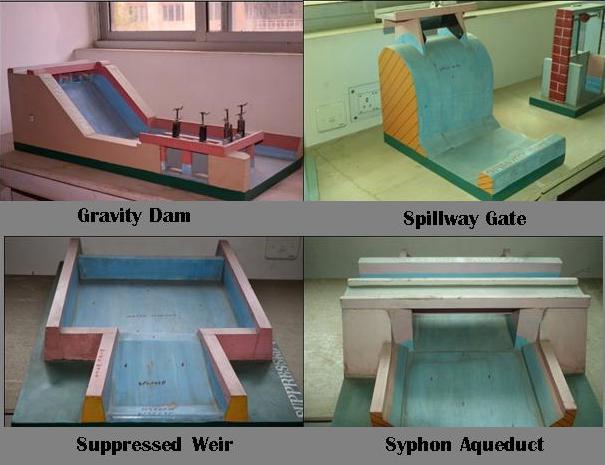
Scaled Models


Venturimeter Test Rig

It is used to find out discharge through a pipe line. Reduction in area at throat results in increase of velocity in steady
flow and thus, decreases in pressure. This decrease in pressure is then noted and discharge is calculated by applying
Bernoulli's equation. Care has to be taken to prevent much reduction in cross sectional area of throat lest it will lead
to cavitation. A smaller angle of divergence is recommended for gradual expansion of flow so that flow separation does
not take place.
Civil Home © 2017 Water Resources Engineering Laboratory, Designed by Sameer Singh/Maintained by Soroj Patowary